BECE 2008 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. A metre rule can be used for measuring the
Solution: A metre rule is designed for linear measurements. It measures length effectively (e.g., tables) but cannot measure volume, curved surfaces (like balls), or small diameters requiring precision tools.
2. Heat travels through vacuum by
Solution: Radiation (infrared waves) transfers heat without a medium. Conduction/convection require matter (solids/fluids), which vacuums lack.
3. A mirror is used to direct sunlight onto the wall of a classroom by
Solution: Mirrors use reflection to redirect light. Dispersion splits light (e.g., prisms), refraction bends it (e.g., lenses), and radiation emits it.
4. Which of the following energy changes takes place in ringing bell?
Solution: Striking a bell converts mechanical energy (kinetic force) into sound energy (vibrations). No significant light or potential energy is involved.
5. A fuse is connected in an electric circuit to
Solution: Fuses melt when current exceeds safe limits, breaking the circuit to prevent damage. They do not increase current/heat or prevent shocks directly.
6. Which of these objects is a magnetic substance?
Solution: Iron is ferromagnetic (attracted to magnets). Aluminium, brass, and copper are non-magnetic metals.
7. Which of the following bodies are natural sources of light?
I. Moon
II. Sun
III. Firefly
Solution: The Sun (fusion) and fireflies (bioluminescence) emit light. The Moon reflects sunlight but produces none.
8. Which of the following statements describes the nature of light?
Solution: Light travels rectilinearly (in straight lines). It can be blocked/absorbed, not all objects are transparent, and reflection depends on surface properties.
9. Metals are able to conduct electricity because they possess
Solution: Free electrons in metals move under voltage, enabling conductivity. Neutrons/protons are bound in nuclei, and atoms alone don’t guarantee conductivity.
10. *Beriberi* is caused by deficiency of vitamin
Solution: Beriberi results from vitamin B₁ (thiamine) deficiency, affecting nerves/heart. Vitamins A, E, K deficiencies cause other issues (e.g., vision, clotting).
11. Which of the following fruits is adapted for dispersal by air?
Solution: Hairy fruits (e.g., dandelions) have structures that catch wind. Succulent fruits attract animals, bright colors lure eaters, and sticky fruits cling.
12. The food substance needed for growth and repair of tissues is
Solution: Proteins provide amino acids for tissue building/repair. Carbohydrates/oils supply energy; vitamins regulate metabolism.
13. The type of teeth used for biting and cutting are the
Solution: Incisors slice/bite food. Canines tear, molars/premolars grind.
14. Water is absorbed by roots in plants and transported to the leaves through the
Solution: Xylem vessels move water/minerals upward. Phloem transports sugars; stomata regulate gas exchange; chlorophyll aids photosynthesis.
15. The outer ear consists of the
Solution: The outer ear includes the pinna (visible part) and eardrum. Ossicles/cochlea are inner/middle ear structures.
16. Changes in pressure in the middle ear is regulated by the
Solution: The Eustachian tube equalizes pressure between the middle ear and throat. Ampullae/cochela handle balance/sound; the eardrum transmits vibrations.
17. The amount of light that enters the eye is reduced by the size of the
Solution: The pupil (opening in the iris) contracts/expands to control light entry. The iris adjusts pupil size; the lens focuses; the retina senses light.
18. In humans, features of parents are passed on to offspring through
Solution: Genetic traits are inherited via reproduction (DNA transfer). Breastfeeding/training/sharing are environmental, not genetic.
19. The taste of water changes when it is boiled because
Solution: Dissolved air (e.g., oxygen) escapes during boiling, altering taste. Heat absorption/evaporation/steam don’t directly affect taste.
20. Arrange the following types of water in order of increasing hardness
I. Tap water
II. Sea water
III. Distilled water
IV. Rain water
Solution: Hardness increases with mineral content: distilled (pure) < rainwater (low minerals) < tap water (moderate) < seawater (high salts).
21. Which of these methods is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids?
Solution: Filtration traps solids (e.g., sand) while liquids pass through. Distillation/evaporation separate solutes; winnowing sorts solids by density.
22. A uniform mixture of two or more metals is called
Solution: Alloys are homogeneous metal mixtures (e.g., brass). Compounds involve chemical bonding; solvents/suspensions are not specific to metals.
23. Which of the following liquids cannot dissolve an oil paint?
Solution: Oil paints dissolve in organic solvents (kerosene, petrol, turpentine) but not in polar water due to "like dissolves like" principle.
24. An atom which contains more electrons than protons becomes a
Solution: Excess electrons create negative ions (anions). Positive ions lack electrons; neutral atoms have balanced charges; compounds involve multiple elements.
25. The following substances are mixtures except
Solution: Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is a pure compound. Air/salt solution/smoke contain multiple components physically mixed.
26. The fish is protected from injury by the
Solution: Scales form a tough, overlapping armor. Fins aid movement; gills enable breathing; operculum covers/protects gills.
27. Which of the following substances is an air pollutant?
Solution: Hydrogen sulphide (H₂S) is toxic/corrosive. Water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen are natural, non-polluting air components.
28. Bathing in lakes and slow moving streams can lead to one getting
Solution: Bilharzia (schistosomiasis) spreads via water-contacting parasite larvae in slow waters. Cholera/dysentery come from contaminated water; river blindness via flies.
29. Some plants shed their leaves during the dry season to prevent
Solution: Leaf shedding (abscission) reduces transpiration, conserving water in droughts. Heat/fire/nutrient loss are not primary reasons.
30. Caterpillar is an example of
Solution: Caterpillars (larval insects) are herbivorous pests that parasitize plants by consuming leaves. They do not infect animals.
31. How long does it take the moon to go completely round the earth?
Solution: The moon’s sidereal orbit (full revolution around Earth) is ~27.3 days, often rounded to 28 days in basic science contexts.
32. An unripe orange is said to be acidic because it
Solution: Acids turn blue litmus red. Bitterness suggests alkalinity (turns red litmus blue); low sugar doesn’t define acidity.
33. The chemical symbol of potassium is
Solution: Potassium’s symbol is K (from Latin *kalium*). N is nitrogen, P is phosphorus, S is sulfur.
34. The property of a metal that makes it possible for it to be drawn into a wire is called
Solution: Ductility allows metals to stretch into wires. Malleability permits shaping (e.g., hammering); conductivity/resistivity relate to electricity.
35. Which of the following methods of preserving food make use of heat energy?
I. Drying
II. Frying
III. Salting
IV. Canning
Solution: Drying (dehydration) and frying use heat to remove moisture/kill microbes. Salting uses osmosis; canning uses heat but option IV is not selected.
36. Weight is an example of
Solution: Weight is the gravitational force on a mass (F = m × g). It is not energy/work (transfer) or power (rate).
37. Blood is prevented from flowing back into the veins by the
Solution: Valves in veins ensure unidirectional blood flow toward the heart. Arteries/capillaries lack valves; the heart pumps but doesn’t block backflow.
38. The force that binds molecules of the same substance together is called
Solution: Cohesion holds like molecules (e.g., water droplets). Adhesion binds different substances; capillary action/surface tension are results of cohesion.
39. Soluble digested food substances enter the blood of the human body by a process called
Solution: Absorption transfers nutrients from the intestines to blood. Ingestion is intake; egestion/excretion remove waste.
40. Capillary action is applied in the following activities except
Solution: Sticking droplets demonstrate adhesion, not capillary action. Capillary action moves liquids through narrow spaces (A, B, C).
1. Question 1
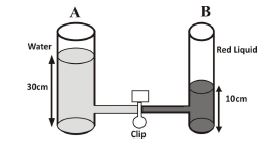
1. (a) In an experiment, two glass containers A and B of different sizes are joined together with a tube and clipped. Water is poured into container A to a height of 30 cm and a red liquid is poured into B to a height of 10 cm. The clip is then removed so that the liquids join together.
(i) State two observations that will be made immediately the clip is removed.
(ii) Explain the observations in (i)
(iii) What two observations will be made after a long time? Explain.
(b) The set-up below is used in the preparation of ammonia gas in the laboratory.
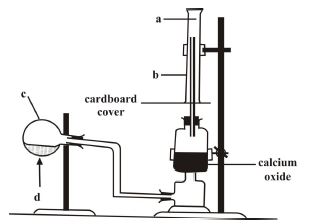
(i) Name the parts labeled a, b and c.
(ii) What is the meaning of the arrow sign d?
(iii) What is the function of the calcium oxide?
(iv) Why has c been tilted downwards?
(v) State the method by which the gas is collected.
(vi) How will you test for the gas?
(vii) Give the names and the chemical formulae of the compounds that form the content of c.
(c) In an experiment, a leaf that is partly green and partly yellow is plucked from a tree and the leaf is:
I. boiled for a minute
II. dipped in warm alcohol
III. washed in cold water
IV. dipped in iodine solution
One part of the leaf turns blue-black after dipping in iodine solution while the other part remains unchanged.
(i) Explain why each of the processes I, II and III is carried out.
(ii) Which part of the leaf turns blue-black? Explain.
(iii) Why does the other part of the leaf not change colour?
(iv) What conclusion can you draw from the experiment?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a) (i) - The height of the red liquid increases.
- The height of the water reduces.
- The red liquid mixes with the water as its particles move into the water.
(ii) - Water has greater pressure due to its height and moves toward lower pressure.
- Diffusion occurs: red liquid molecules move from higher concentration to lower concentration in water.
(iii) - A uniform mixture with consistent color and concentration forms.
- Due to capillarity, liquid level in smaller container (B) becomes slightly higher than in container A.
(b) (i) - a: Ammonia gas
- b: Gas jar
- c: Round-bottomed flask
(ii) - d: Heat (indicates heating of the flask)
(iii) - Removes moisture/water from the gas.
(iv) - Prevents condensed water from flowing back into the hot flask.
(v) - Upward delivery (downward displacement of air).
(vi) - Pungent smell
- Moist red litmus paper turns blue
- Produces fumes with concentrated HCl
(vii) - Alkali + Ammonium chloride (e.g., NaOH + NH₄Cl, Ca(OH)₂ + NH₄Cl, KOH + NH₄Cl, Mg(OH)₂ + NH₄Cl)
(c) (i) - I: Stops photosynthesis by killing cells.
- II: Removes chlorophyll.
- III: Washes away alcohol and softens the leaf.
(ii) - The green part (presence of starch from photosynthesis).
(iii) - Yellow part lacks chlorophyll/starch; no photosynthesis occurred.
(iv) - Chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
2. Question 2
2. (a) (i) State the difference between an opaque object and a translucent object.
(ii) Give one example each of an opaque and a translucent material.
(b) (i) What is the importance of seed dispersal?
(ii) Name two types of fruits and state their mode of dispersal.
(c) (i) What is recycling?
(ii) Give two advantages of recycling of materials.
(iii) List three recycled products in Ghana.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a) (i) - Opaque: Blocks all light. Translucent: Allows partial/diffused light.
(ii) - Opaque: Wood, metal, mirror, earth, mammals.
- Translucent: Fabric, frosted glass, oily paper, lightly-colored water.
(b) (i) - Prevents overcrowding.
- Reduces plant disease spread.
- Avoids competition for nutrients.
- Enables growth in new areas.
(ii) - Tridax/silk cotton: Wind
- Coconut: Water
- Orange/guava: Animals
- Cowpea/crotalaria: Explosive mechanism
(c) (i) - Converting waste into new useful products.
(ii) - Reduces environmental pollution.
- Creates jobs/income.
- Saves money on waste control.
- Conserves resources.
- Generates energy.
(iii) - Paper, biogas, polythene, rubber, particle boards, iron rods.
3. Question 3
3. (a) (i) Explain the term bedwetting.
(ii) State two diseases that may result from bedwetting.
(b) (i) State the difference between hard water and impure water.
(ii) Give the stages involved in the treatment of water for a community.
(c) A piece of stone has a mass of 36.0 g. When put into water in a glass container, the water level rises from 60.0 cm³ to 90.0 cm³.
(i) Calculate the density of the stone.
(ii) Explain what will be observed when the stone is put into another liquid of density 1.4 g/cm³.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) (i) - Involuntary urination during sleep.
(ii) - Ringworm, skin rash, eczema.
(b) (i) - Hard water: Does not lather easily with soap.
- Impure water: Unwholesome for drinking (contains harmful substances).
(ii) - Filtration to remove suspended materials.
- Adding alum for sedimentation.
- Chlorination to kill germs.
- Aeration to remove odors.
(c) (i) - Volume = 90.0 cm³ - 60.0 cm³ = 30.0 cm³
- Density = 36.0 g / 30.0 cm³ = 1.2 g/cm³
(ii) - Stone (1.2 g/cm³) is less dense than liquid (1.4 g/cm³), so it floats.
4. Question 4
4. (a) (i) What is an echo?
(ii) State two uses of echoes.
(b) (i) State three diseases that affect the respiratory system.
(ii) Name one method each to prevent these diseases.
(c) (i) What is biotechnology?
(ii) List three products from biotechnology.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) - Reflection of sound waves from a hard surface.
(ii) - Measuring distances (e.g., bats, seabed depth).
- Ultrasound for medical diagnosis.
- Mineral exploration.
- Obstacle detection by ships.
- Measuring sound velocity.
(b) (i) - Tuberculosis, asthma, pneumonia, common cold, lung cancer, whooping cough.
(ii) - Tuberculosis: Avoid sharing utensils with infected persons.
- Asthma: Avoid dust/pollen.
- Pneumonia: Wear warm clothes.
- Common cold: Avoid cold/dusty air.
- Lung cancer: Avoid smoking.
- Whooping cough: Vaccination.
(c) (i) - Using biological processes for human benefit.
(ii) - Cheese, yogurt, wine, beer, vaccines, insulin, antibiotics, biogas, bread.
5. QUESTION 5
5. (a) (i) Define pressure.
(ii) State three applications of pressure in everyday life.
(b) State four functions of the liver in digestion.
(c) (i) What is a compound?
(ii) Give two properties of a compound.
(iii) Write the name and chemical formula for:
(a) Hydrogen and chlorine
(b) Magnesium and oxygen.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5. (a) (i) - Force per unit area (Pressure = Force / Area).
(ii) - Pumping car tires.
- Opening sealed cans with a knife.
- Drawing liquid with a syringe/straw.
- Pumping liquid to higher levels.
(b) - Produces bile to emulsify fats.
- Converts glycogen to glucose.
- Stores excess glucose as glycogen.
- Removes excess glucose from blood.
(c) (i) - Chemically combined elements in fixed proportions.
(ii) - Properties differ from constituent elements.
- Fixed composition ratio.
- Formed with heat changes.
- Cannot be separated physically.
(iii) (a) - Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
(b) - Magnesium oxide (MgO)